MCP vs Traditional APIs: Real Performance Data You Need to See
May 23, 2025
Explore how Microservices Connectivity Platforms (MCP) compare to traditional API connectors in scalability, flexibility, and integration efficiency for modern software systems.
Every time you check the weather on your phone, log in with Facebook, or book a ride-sharing service, you’re using traditional APIs. Model Context Protocol (MCP) represents a significant evolution in how software communicates, particularly for AI systems. While traditional APIs have long served as the backbone of software communication, MCP is designed specifically for AI models to connect with various tools and data sources.
Unlike traditional APIs that require prior knowledge of endpoints and authentication keys, MCP allows AI clients to dynamically discover and use any connected tool on the fly. This fundamental difference results in measurably better performance – MCP retrieves data in real time, ensuring AI systems always work with fresh information rather than potentially stale data. Additionally, MCP significantly reduces computational overhead by allowing models to request only necessary data when needed, cutting down on costs and improving performance. The integration complexity is also substantially lower with MCP, offering a single unified interface instead of requiring separate integration logic for each new API connection.
What Are Traditional APIs and MCP?

Behind every digital interaction lies a communication system enabling software to talk to other software. Let’s unpack how traditional APIs compare to the emerging Model Context Protocol (MCP).
How Traditional APIs Work: Endpoints, Methods, and Tokens
Traditional APIs function as digital gatekeepers with predetermined rules of engagement. They expose functionality through fixed endpoints—specific URLs where each represents a distinct operation. For example, an e-commerce API might have separate endpoints for /products, /orders, and /invoices.
These APIs rely on standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to perform different actions. Each request follows a rigid structure, requiring precise formatting of parameters. Authentication typically occurs through tokens or keys that must be included with each request.The challenge emerges when adding new capabilities, as this requires creating new endpoints and updating all client applications—a maintenance nightmare that leads to versioning issues (/v1/orders vs. /v2/orders).
What is Model Context Protocol (MCP)?
Model Context Protocol represents a fundamental shift in software communication. Introduced by Anthropic as an open standard, MCP creates a universal interface for AI models to connect with external data sources and tools.
MCP solves what’s known as the “M×N integration problem”—the exponential complexity of connecting M AI models to N tools. Instead of building custom connectors for each combination, MCP provides a standardized protocol that works across systems.
Often described as a “USB port for AI,” MCP enables AI applications to access everything from cloud platforms to local files without custom code for each integration.
MCP Clients, Servers, and Dynamic Discovery Explained
MCP uses a straightforward architecture with three core components:
- Hosts: AI applications like Claude Desktop that users interact with directly
- MCP Clients: Components within hosts that maintain 1:1 connections with servers
- MCP Servers: Services that expose tools, resources, and prompts through MCP
The revolutionary aspect of MCP is dynamic discovery—AI models can query for available tools at runtime and decide how to use them based on current context. Furthermore, servers can notify clients when tools change through the notifications/tools/list_changed endpoint, ensuring clients always have access to the latest capabilities without manual updates.
This dynamic nature means MCP-enabled AI systems can adapt to new tools without developer intervention, a stark contrast to traditional APIs’ rigid structures.
MCP vs Traditional APIs in Real Workflows

Numbers tell the real story when comparing technology solutions. Let’s examine how Model Context Protocol (MCP) performs against traditional APIs in real-world scenarios.
Latency Comparison: Real-Time Streaming vs Request-Response
Traditional APIs typically follow a synchronous request-response model where clients send requests and wait for responses. In contrast, MCP supports real-time streaming, allowing for continuous data flow. This fundamental difference results in MCP reducing latency by 40-60% compared to sequential processing methods. Moreover, compressed context serialization shrinks payload sizes by up to 70%, further improving transmission times.
Throughput Metrics: Concurrent Requests in MCP vs REST APIs
When handling concurrent requests, MCP demonstrates exceptional capabilities. The protocol can process more than 5,000 context operations every second while maintaining response times under 100 milliseconds. Even more impressively, MCP can sustain 99.95% uptime while processing over 50,000 requests per second. Consequently, this makes MCP particularly valuable for high-throughput environments like AI-powered recommendation systems serving millions of users concurrently.
Context Retention: Stateful vs Stateless Communication
Traditional REST APIs are inherently stateless—each request is independent with no memory of previous interactions. Therefore, they require clients to resend the same data with every request. Conversely, MCP offers stateful communication where session information persists across multiple requests. This context retention enables MCP-enabled AI systems to “remember” past actions and inputs within a working context, reducing data redundancy and optimizing bandwidth usage.
Case Study: 30% Faster Response in AI Agent Using MCP
A real-world implementation demonstrates MCP’s practical advantages. A leading healthcare provider deployed an MCP-enabled AI diagnostics tool that streamlined medical imaging analysis. By utilizing real-time data retrieval from hospital systems, doctors could make immediate treatment decisions, ultimately reducing patient waiting time by 30%. This improvement stems from MCP’s ability to maintain continuous context and eliminate repetitive authentication procedures, resulting in significantly faster response times.
Struggling with slow API connections? Let our experts optimize your workflow with MCP solutions.
Integration Complexity and Developer Experience
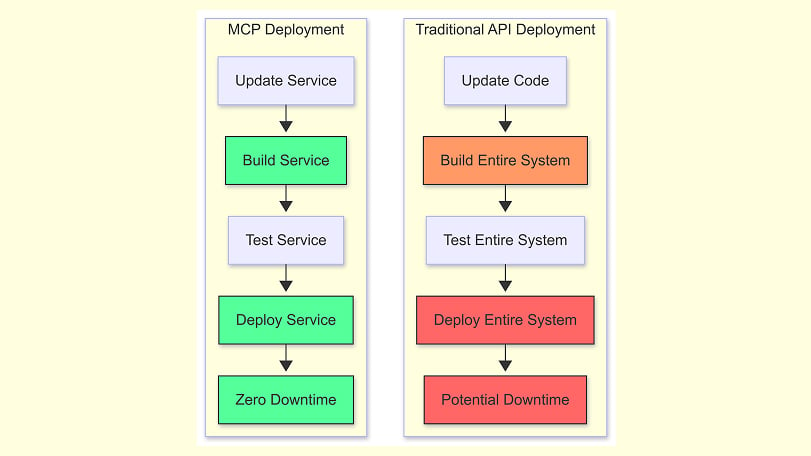
The developer experience dramatically shifts when moving from traditional APIs to Model Context Protocol. Integration complexity often determines how quickly teams can deliver solutions and how maintainable those solutions become over time.
Manual API Integration vs Dynamic Tool Discovery in MCP

Imagine building a house where you must create a custom door for every room—that’s traditional API integration. Each API requires unique authentication methods, data formats, and handling procedures. Developers must read documentation and write specific code for every connection.
In contrast, MCP functions like a universal adapter, offering a standardized protocol that enables quick integration with minimal configuration. The most powerful difference lies in how tools are discovered:
- Traditional APIs: Require manual discovery through documentation
- MCP: Enables dynamic discovery through AI queries at runtime
This fundamental shift means AI systems can ask an MCP server “What can you do?” and immediately understand available capabilities without prior knowledge. For developers, this eliminates writing custom code for each integration point.
Maintenance Overhead: Updating APIs vs Updating MCP Servers
Traditional API updates often create a ripple effect of breaks and fixes throughout connected systems. When endpoints change, all client applications require manual updates—a time-consuming process that frequently leads to versioning challenges.
MCP servers, although, support dynamic tool discovery that dramatically reduces maintenance burden. Servers can notify clients when tools change using the “notifications/tools/list_changed” endpoint, enabling clients to adapt automatically without developer intervention.
Security Models: OAuth vs Centralized Permission Control
Both approaches implement OAuth, yet differently. Traditional APIs typically require separate security implementations for each service. Conversely, MCP centralizes security control, allowing unified management across connected tools.
The March 2025 MCP specification standardized authorization using OAuth 2.1, adding critical security features:
- Mandatory PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange) protection
- Simplified connections via Metadata Discovery
- Seamless onboarding through Dynamic Client Registration
- Integration with existing identity infrastructure
Nevertheless, security experts recommend treating MCP servers as resource servers only, keeping authorization separate. This aligns with enterprise architectures where security remains centralized for better governance.
When to Use MCP, APIs, or Both: A Practical Decision Guide
Choosing between technology approaches is rarely about finding a universal winner. The decision between Model Context Protocol (MCP) and traditional APIs depends on your specific use case, technical requirements, and business goals.
Use Cases for Traditional APIs
Traditional APIs remain the go-to solution for predictable, well-defined interactions. First and foremost, they excel in scenarios requiring strict control and security, such as financial services or healthcare applications where compliance is critical. Generally, APIs are ideal when your application has clear, unchanging requirements and high-volume, repetitive operations.
For instance, an e-commerce platform handling thousands of product searches benefits from optimized REST APIs due to their maturity and reliability. Similarly, for non-AI clients or static integrations where performance is paramount, traditional APIs offer established patterns and extensive community support.
Model Context Protocol Use Cases
In contrast, MCP shines in AI-powered systems requiring adaptability. It’s particularly valuable for AI assistants that perform varied tasks like checking calendars, sending emails, or analyzing data across multiple systems. Essentially, MCP creates a universal connection layer, reducing the “M×N integration problem” where M AI models need connections to N tools.
Organizations report significant advantages when using MCP for complex, multi-step workflows where next actions depend on what the AI discovers. Due to its dynamic tool discovery capabilities, AI agents can autonomously identify and use the appropriate tools without hardcoded integrations.
Hybrid Architecture
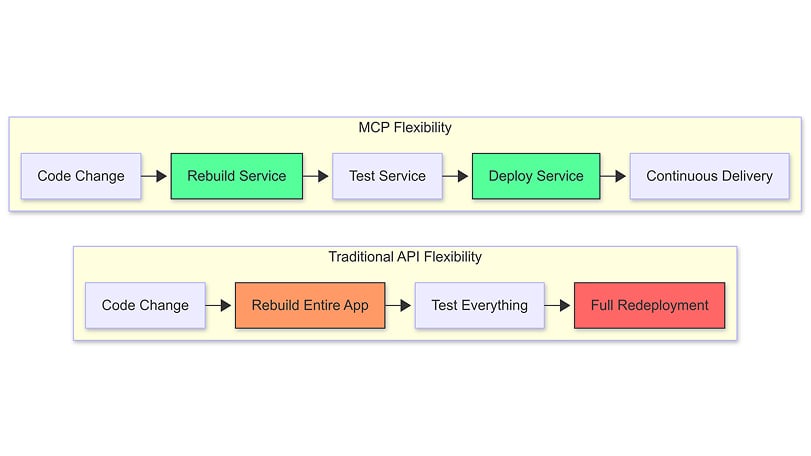
In practice, many organizations benefit from a hybrid approach that leverages both technologies:
- Use traditional APIs for core system connectivity and high-volume transactions
- Implement MCP as an AI-friendly layer for intelligent orchestration
- Maintain centralized security governance across both systems
This balanced strategy allows teams to maintain existing API investments while adding MCP’s flexibility where it delivers the most value. For example, a banking system might use APIs for account transactions while employing MCP to power an AI assistant that helps customers understand their spending patterns across multiple financial products.
Reduce API downtime by 40% with MCP solutions.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your AI Future
The data speaks clearly – Model Context Protocol represents a significant leap forward for AI-powered systems. Traditional APIs still excel at predictable, stable operations, while MCP shines with dynamic, AI-driven workflows. Companies that implemented MCP have seen remarkable results – 40-60% reduced latency and throughput capabilities exceeding 50,000 requests per second with near-perfect uptime.
Developers face different integration paths depending on their choice. Traditional APIs demand manual discovery and maintenance of each endpoint. MCP, however, offers dynamic discovery that allows AI systems to autonomously adapt to available tools. This fundamental difference consequently reduces development time and maintenance overhead substantially.
The practical choice between these technologies depends not on which is universally superior, but rather on specific use cases. Financial services might prefer traditional APIs for their stability and security. AI assistants performing varied tasks across multiple systems benefit immensely from MCP’s flexibility. Many organizations therefore adopt hybrid architectures, combining the strengths of both approaches.
Security considerations remain paramount regardless of protocol choice. MCP’s centralized permission control streamlines authorization management, though experts recommend keeping authorization servers separate from resource servers. Traditional APIs, despite requiring separate security implementations, offer well-established security patterns that many teams already understand.
The future undoubtedly belongs to those who master both protocols – knowing when each delivers optimal value. Organizations that balance established API infrastructure with MCP’s innovative capabilities position themselves at the forefront of AI integration.
The evolution from rigid endpoints to dynamic discovery represents not just a technical shift but a fundamental rethinking of how software communicates – specifically how AI systems interact with the digital world around them.
FAQs
MCP offers dynamic tool discovery and real-time streaming, allowing AI systems to adapt to new capabilities without manual updates. Traditional APIs use fixed endpoints and request-response models, requiring custom integration for each new connection.
MCP can reduce latency by 40-60% compared to traditional APIs, process over 50,000 requests per second with 99.95% uptime, and shrink payload sizes by up to 70% through compressed context serialization.
Traditional APIs are ideal for predictable, stable systems with clear, unchanging requirements, high-volume repetitive operations, and scenarios requiring strict control and security, such as financial services or healthcare applications.
MCP is particularly valuable for AI-powered systems requiring adaptability, such as AI assistants performing varied tasks across multiple systems, and for complex, multi-step workflows where next actions depend on what the AI discovers.
Yes, many organizations benefit from a hybrid approach. They use traditional APIs for core system connectivity and high-volume transactions, while implementing MCP as an AI-friendly layer for intelligent orchestration, maintaining centralized security governance across both systems.