
Software development is a booming industry, and apps have become an integral part of our daily lives, including in healthcare.
With healthcare apps, both patients and medical professionals can access quality services conveniently, avoiding long wait times for short appointments.
The need for healthcare software development is on the rise and as per McKinsey, digital innovation will boost the healthcare sector’s value to $350-410 billion by 2025.
Over the past decade, healthcare software has brought significant growth, transforming the way hospitals operate. Now, accessing the latest health reports is as easy as a few taps and clicks.
Electronic medical records (EMRs) and electronic health records (EHRs) are important advancements in healthcare technology. Despite having distinct objectives, these terms are often used interchangeably.
So, it’s essential to understand the difference between EMR and EHR. Before we dive into the dissimilarities, let’s get a quick overview of what each of them is.
What is the EMR System in Healthcare?

In healthcare, an Electronic Medical Record (EMR) system is like a digital version of a patient’s medical chart. Instead of old-fashioned paper charts, it’s a place where all their medical history is stored in an easy-to-use digital format.
Here’s a breakdown of what EMR systems offer:
Features:
Complete Health Records:
It keeps lots of information like age, health conditions, allergies, medicines, vaccinations, test results, X-ray reports, notes from the doctor, and more.
Improved Visibility and Accessibility:
Doctors and nurses can quickly look at a patient’s records from any allowed device. This helps them make smart decisions and keep providing good care.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration:
Lets healthcare providers securely talk to each other, making it easier for doctors, nurses, and specialists to work together and avoid confusion.
Patient Engagement and Education:
Some EMR systems provide patients with online access to their records, empowering them to understand their health and participate in decision-making.
Prescription Management and Drug Interaction Alerts:
Makes it easier to order and give out prescriptions, lowers the risk of medication mistakes, and spots potential issues with drug interactions.
Improved Reporting and Quality Control:
Facilitates data analysis and reporting, providing valuable insights into clinical practice and quality of care.
Benefits of EMR Systems:
Improved patient outcomes:
Early detection of potential issues, better medication management, and more effective care coordination, leading to better health results for patients.
Improved prescription procedure:
Electronic medical records have a special filter that prevents doctors from recommending treatments or drugs with bad side effects, ensuring patient safety.
Increased efficiency and productivity:
EMRs save time and effort for healthcare providers, letting them see more patients and work more smoothly.
Reduced healthcare costs:
By minimizing errors and making processes smoother, EMRs can help reduce overall healthcare costs.
Enhanced patient satisfaction:
Patients like the convenience and improved communication that comes with EMRs.
- It’s crucial to understand that EMR systems and Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are not the same:
- EMRs mainly deal with the medical history of individual patients in a specific practice or clinic.
- EHRs go further by adding more details, like patient demographics and administrative data, and are usually shared among various healthcare providers and institutions.
- Overall, EMR systems are a valuable tool that has changed healthcare delivery. They bring lots of advantages for both patients and providers, and more and more people are using them.
Applications of EMR systems
EMR systems do more than store medical records. Now, they do many things to assist doctors and engage patients, making the overall healthcare experience better. Let’s discuss some key things they can do:
For Clinical Care:
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS):
EMRs can use CDSS to analyze patient data and suggest diagnoses, treatment options, and medication doses based on evidence-based guidelines. This helps doctors make decisions and encourages following the best healthcare practices.
Order Entry and Tracking:
With EMRs, doctors can electronically order and track prescriptions, lab tests, and other procedures. This cuts down on mistakes, speeds up tasks, and improves communication among healthcare teams.
Managing Long-Term Health Conditions:
EMRs can keep an eye on vital signs if patients are taking their medications and other info for chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease. This helps in actively managing the condition and stopping problems.
Public Health Reporting:
EMR data can be brought together and made anonymous to spot trends and patterns in disease outbreaks. This info helps plan public health efforts and support research.
For Patient Engagement:
Patient Portal Access:
Patients can go online to see their medical records, check lab results, book appointments, and talk with their healthcare providers. This helps patients get involved in their care and take charge.
Medication Management Tools:
EMRs can remind patients to take their medications, help them refill prescriptions, and give educational info. This encourages patients to stick to their medication plans and get better.
Remote Monitoring and Virtual Health:
Some EMRs let doctors keep an eye on vital signs for certain conditions from a distance. This allows for telehealth consultations and taking action early if needed.
For Research and Analytics:
Big Data and Clinical Research:
EMR data can be brought together and studied for research, offering valuable insights into how diseases work, how well treatments work, and trends in the health of populations.
Quality Improvement:
EMR data helps keep track of important indicators, find places where things can get better, and make clinical practices work better in healthcare organizations.
Personalized Medicine:
EMRs, by looking at individual patient data, can assist in creating treatment plans that fit specific needs and genetic backgrounds. This opens the door to personalized approaches in medicine.
Also, EMRs can help with:
Administrative tasks:
Things like billing, checking insurance, and scheduling can be made simpler with integrated features, making things work better and lowering mistakes.
Following rules and regulations:
EMRs can make it easier to follow data privacy rules and reporting requirements.
The uses of EMR systems keep changing as technology gets better and healthcare needs move. Using these new tools can help healthcare providers give better care, give patients more control, and make healthcare work better with data.
What is EHR in Healthcare?

An EHR, or Electronic Health Record, is like a digital book containing all your health information. It’s stored securely and can be accessed by authorized healthcare providers.
Think of an EHR as a supercharged paper chart with special abilities:
- Comprehensive: It holds all your details, from allergies to medications, tests, and more.
- Real-time: Updates happen instantly, making sure your doctors have the latest info for your care.
- Accessible: Authorized providers can check it from anywhere, avoiding duplicate tests and keeping everyone informed.
- Secure: Your EHR follows strict privacy laws and security to keep your information safe.
EHRs bring a multitude of advantages for both patients and healthcare providers:

For patients:
Enhanced care coordination:
Your healthcare team can effortlessly exchange information and work together on your care plan.
Minimized medication errors:
EHRs can automatically screen for medication interactions and allergies, reducing the risk of medication errors.
Informed decision-making:
You can access your own EHR to gain insights into your health, enabling you to make well-informed decisions about your care.
For healthcare providers:
Increased efficiency:
EHRs can automate tasks and simplify workflows, allowing providers to dedicate more time to patient care.
Lower healthcare costs:
EHRs contribute to cost reduction by preventing redundant tests and enhancing care coordination.
Enhanced quality of care:
EHRs equip providers with data and tools to elevate the quality of care they provide.
Overall, EHRs are a valuable tool that improves patient care, making it easier and more efficient to receive the necessary treatment.
What is the Difference Between EMR and EHR?
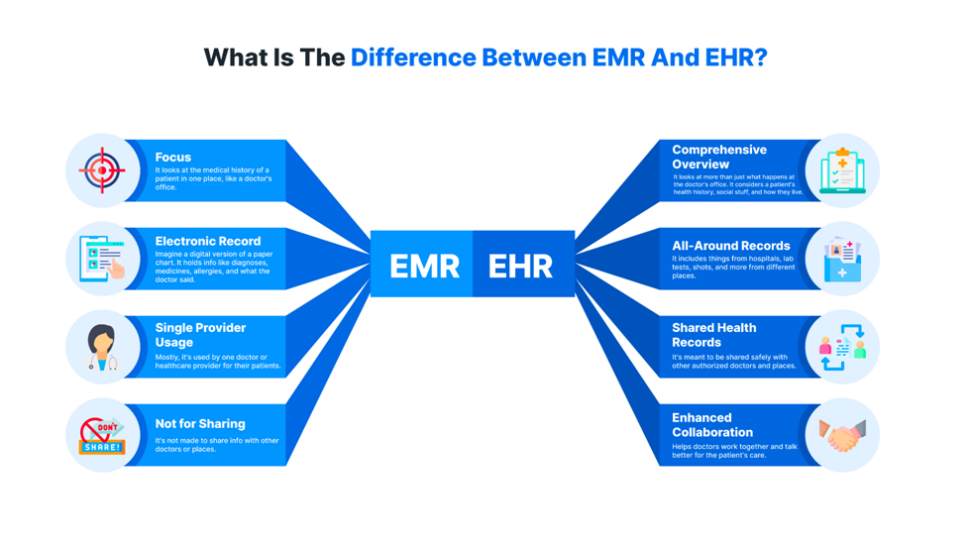
EHR and EMR are often used interchangeably, but there are some key differences between them.
Here’s a breakdown:
EMR (Electronic Medical Record)
- Focus: It looks at the medical history of a patient in one place, like a doctor’s office.
- Electronic Record: Imagine a digital version of a paper chart. It holds info like diagnoses, medicines, allergies, and what the doctor said.
- Single Provider Usage: Mostly, it’s used by one doctor or healthcare provider for their patients.
- Not for Sharing: It’s not made to share info with other doctors or places.
EHR (Electronic Health Record)
- Comprehensive Overview: It looks at more than just what happens at the doctor’s office. It considers a patient’s health history, social stuff, and how they live.
- All-Around Records: It includes things from hospitals, lab tests, shots, and more from different places.
- Shared Health Records: It’s meant to be shared safely with other authorized doctors and places.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Helps doctors work together and talk better for the patient’s care.
Let’s use an analogy to grasp the distinction:
Imagine EMR as a private diary readable by one person, holding details about a patient in a specific context.
Now, envision EHR as an open book shared among authorized individuals. It offers a broader view of a patient’s health story across various settings.
In short:
- EMR is for internal use within a single practice.
- EHR is for broader sharing and coordinated care across different healthcare providers.
EMR Software Development Vs EHR Software Development
Deciding between EMR Software Development and EHR software development relies on your particular needs and the people you want to reach. Here’s a breakdown of the main differences to assist you in making a choice:
Focus:
- EMR software: Looks at one healthcare spot. Keeps things about patients inside, like notes, diagnoses, medicines, and appointments.
- EHR software: Looks at a patient’s broader health across different healthcare providers and institutions. Takes in data from clinics, hospitals, labs, pharmacies, and more.
Features:
- EMR software: Does basic things like scheduling appointments, keeping records, and handling bills. Might not work very well with other systems.
- EHR software: Does advanced things like managing medicines, ordering lab tests, handling telehealth, setting up patient portals, looking at overall population health, and working smoothly with other healthcare systems.
Integration
- EMR software: Limited integration with other systems, mainly within the same practice.
- EHR software: Focuses more on working well with other systems and sharing data. This includes hospitals, labs, and pharmacies.
Security and Compliance
- EMR software: Needs to stick to basic rules from HIPAA for keeping patient info private.
- EHR software: Follows Strict Rules: Has to stick to even stricter rules from HIPAA, especially when sending and sharing data across different places.
Development Cost
- EMR software: Generally cheaper to develop due to fewer features and simpler functionality.
- EHR software: More expensive to develop due to complex features and strict security and compliance needs.
Target Audience
- EMR software: Best for little clinics or single doctors who don’t need to share lots of data.
- EHR software: Great for big healthcare places, hospitals, clinics with many specialties, and networks that need to work together and share data.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | EMR Software | EHR Software |
| Focus | Individual practice or facility | Effective data-sharing capability |
| Features | Basic | Advanced |
| Integration | Limited | Effective data sharing capability |
| Security/Compliance | Basic HIPAA | Stricter HIPAA |
| Development Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Target Audience | Small clinics, specialists, independents | Large organizations, hospitals, networks |
In the end, the right decision depends on what you need and what you have. Think about who you’re helping, how much information you need to share, what features you want, and how much money you can spend before you choose between EMR and EHR software.
What Should You Choose for Your Healthcare Business?
Understanding the difference between EHR and EMR is crucial for choosing the right system for healthcare.
EHR, being interconnected and accessible at various care points, enhances both healthcare quality and patient satisfaction. EMR, while better than paper records, may only improve healthcare quality.
Healthcare companies are now encouraged to use compatible medical software, leading to increased EHR adoption. Choosing medical software is like picking any other technology, and employee input is valuable. Consider your healthcare facility’s specific goals and needs.
For routine information sharing, especially outside your clinic, using accredited EHR technology is wise.
However, if your practice is independent and focused on a specific medical issue, an EMR might be a simple and suitable addition to your information systems.
How Ailoitte Can Help You Choose the Best EMR/EHR for Your Healthcare Business?
The future of the medical field is in healthcare software. This software is driving a revolution in healthcare by making administration smoother, boosting efficiency, and cutting down on costs. Investing in comprehensive software applications is essential.
For top-notch and advanced improvements in preventive, prescriptive, and secure healthcare, rely on Ailoitte’s healthcare software development services. We know how important it is to create services and apps that enhance patient care, make medical treatment better, and provide creative solutions.
Contact us to get a customized solution for your facility, making patients happier and streamlining administrative processes.
Conclusion
In summary, both EMR and EHR lay the groundwork for the future of medical practice by making data collection and processing more effective.
Today, EHR adoption has outpaced EMR, empowering patients to play a more active role and control their clinical records. This leads to a more informed and healthier population!
When used correctly, EHR offers advantages over EMRs, often leading to improvements.
Therefore, healthcare facilities should prioritize regulating and managing EHR systems to best serve the patient’s interests, considering that paper records are becoming outdated.
FAQs
EMR is like a digital file for one doctor’s office, while EHR lets doctors easily share information with others. EMR focuses on medical history, and EHR gives a complete picture of a patient’s overall health.
Medical software is crucial for modern healthcare. It replaces messy paper records and simplifies tasks like handling patient information and medical claims. Both EMR and EHR are good options, and your choice depends on your organization’s needs.
EMR software development is the creation of digital tools for patients and healthcare workers to access medical information. It includes features like electronic communication and record-keeping to enhance communication between healthcare providers and patients.
People often use the terms EMR and EHR interchangeably, but there’s a significant difference. EMRs were initially focused on medical data for diagnosis and treatment, while EHRs cover a broader spectrum of health information from various providers, making them more advanced.
Often, both. Hospitals use EHRs to share patient data among multiple physicians. They also use EMRs, managed by a single provider.
Leave a Reply
Hire Dedicated Healthcare IT Experts
Get our services on time and within budget.


















.png)
.png)
.png)



Leave a Comment