An expert understanding of Proof of Concept (PoC) vs. Prototype vs. Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is essential to ensure the achievement of your product development goals. The success of all three strategies depends on their timely and correct execution.
All three strategies are becoming mainstream in many small and large businesses.
An informative piece by 101 Blockchains claims that companies like DHL and Pfizer use proof-of-concept for various development projects.
Prototyping also becomes a business strategy for many startups and grows every day. According to Fortune Business Insights, the rapid prototyping materials will reach $1,496 million in 2028 compared to $497 million in 2021.
And Purrweb provides notable examples of minimum viable products. One of which is Amazon. Amazon was a minimum viable product in the 1990s when Jeff Bezos started as an online bookstore.
Bezos improved on that MVP product and kept adding new products and categories on the platform to sell. The strategy eventually helped Amazon become one of the top e-commerce platforms in the world.
These strategies all have benefits if you use them correctly. That is why you must learn about them carefully to understand their applications.
What is Proof of Concept (POC)?
Proof of Concept is an early development process that evaluates the feasibility of a product idea in practical applications.
Proof of concept in software development provides a thorough assessment of your software idea, whether you can turn that idea into reality, and whether people want the end product that comes from it.
PoC Features
Proof of concept is a professional way to determine whether your idea has what it takes to make it in the competitive market. And survive the risks associated with the development and post-development stage.
PoC helps you:
- Determine the feasibility of your idea.
- Reveal the potential of your product idea.
- Reveals the risks associated with the development stage.
- Helps identify the demand for the product/service that will result from your product idea.
POC Benefits
1. New Investors
A well-developed POC can attract investors and make it easy for them to trust the potential of a tested idea.
2. Economical
The cost of Proof of Concept (POC) development is inexpensive as compared to MVP and prototype and perfect for startups and small businesses.
It can quickly help you determine whether your project is ready for development and its average duration.
3. Multi-project Compatibility and Lack of Risks
You can create POCs for multiple projects to ensure their success. And reduce the risks associated with their process.
4. Competitive Advantage
A good POC strategy will help you stay ahead of the competition. And make your product/service stand out after launch.
What is a Prototype?
A prototype is an early version of the product/service that helps the users see how your product/service will look and feel. The prototype comes after a POC analysis is completed.
If you are developing an app, a prototype is a basic iteration that helps you understand its UI/UX and feature requirements.
A software prototype shows the results of POC analysis, what your product will look like, how you can make it better, and its weak points.
Types of Prototype Models
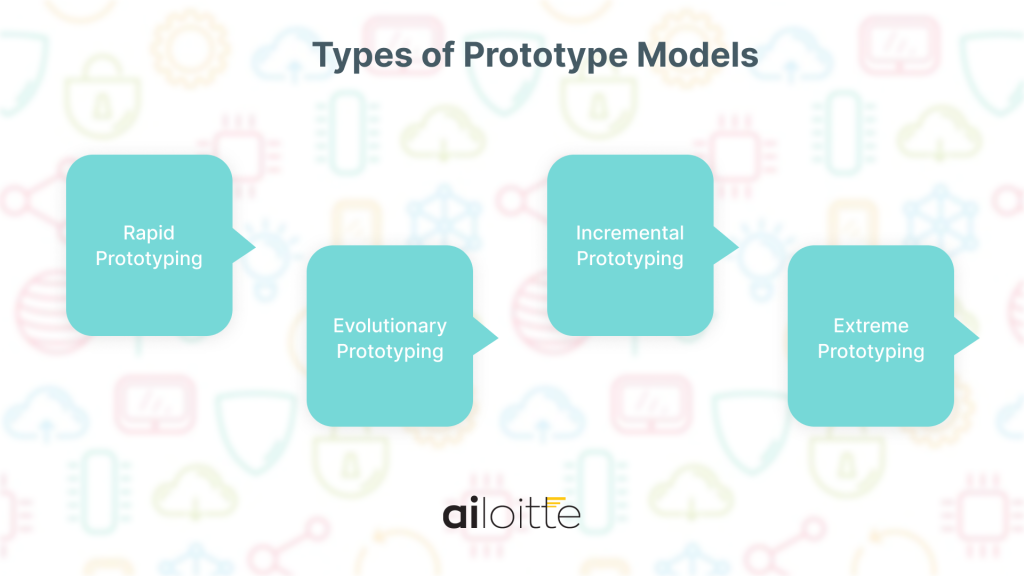
1. Rapid Prototyping
The team develops a rapid prototype with initial product requirements. It’s a quick prototype solution that determines whether you can turn it into the final product by implementing user feedback. Or be rejected and forced to come up with something better.
2. Evolutionary Prototyping
Evolutionary prototyping is a process where every prototype helps the development of a better prototype after receiving user feedback.
3. Incremental Prototyping
Incremental prototyping is an approach where the developers divide the project into small parts and develop a prototype for every one of those parts.
These prototypes are then merged into one to create a comprehensive prototype.
4. Extreme Prototyping
Extreme prototyping is the development of various web prototypes in HTML format with a services layer. The process tests the web prototypes, implements the services, and then integrates them into the final product.
Prototyping Features
- Reveals design and development flaws.
- It identifies the needs of customers in the early stages.
- It integrates complex ideas into one comprehensive format.
- You can use it for multiple projects in many different sectors.
Prototyping Benefits
- It effectively explains product workflow to users.
- Shows a visual example of your product’s look and functionality before the actual development begins.
- Prototype development provides early feedback on your product/service.
- A prototype helps identify flaws in your product before you begin development.
- It saves money by solving problems in the early stages instead of after development.
- The prototype development cost is lower than MVP development and more than PoC.
- It prevents a situation where it is too late or too expensive to make new changes.
- It rejuvenates the faith of investors in your product/service.
- Stakeholders and investors can suggest changes if required.
- Determines whether the product/service will create demand in the market or not.
- Feedback from users, investors, stakeholders, and the team will lead to a product/service that makes a mark in the market and meets company requirements.
What is a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)?
A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a functional product with only core features. When differentiating Minimum viable product vs. prototype vs. POC, it’s vital to understand how they are related. MVP is the next stage after POC and Prototype. MVP presents the first version of the product that users can use and find out how it can help them.
For example, a sketch is a minimum viable product if a painting is a final product.
The minimum viable product helps you validate product usability, feasibility, internal/external assumptions, and market demand.
Minimum Viable Product Features
A minimum viable product has only the core feature to support the stable and helpful functionality of a product. For example, MVP features would include Order Food, Search, Location, Cancel Order, Menu Lists, and Customer Care if your product is a food delivery app.
The advanced features in such apps are Track Delivery Executive, Restaurant Recommendations, Call Restaurant, and Add Multiple Addresses.
MVP Benefits
- You can get it ready for launch with minimum effort and in a short time.
- MVP development for apps, software, or products involves core features that meet the initial needs of users.
- MVP development cost is substantially lower than that for the final product i.e., mobile application or software. In that, it prevents unnecessary development costs and time.
- It shows the right direction for the further development of your product.
- It verifies product feasibility and POC analysis.
- Provides proper user feedback and helps implement the changes in the advanced version.
- You can test your product on the users with minimum effort and time.
- If users are satisfied with only the core features of a product, then you know the advanced version of your product will do wonders.
- Reveal the strong and weak points of your product with user feedback.
- Reveal the aspects that can make your product unique and convenient for users.
- It brings more investors and helps the product grow.
- A good MVP product promotes a “word of mouth” marketing strategy.
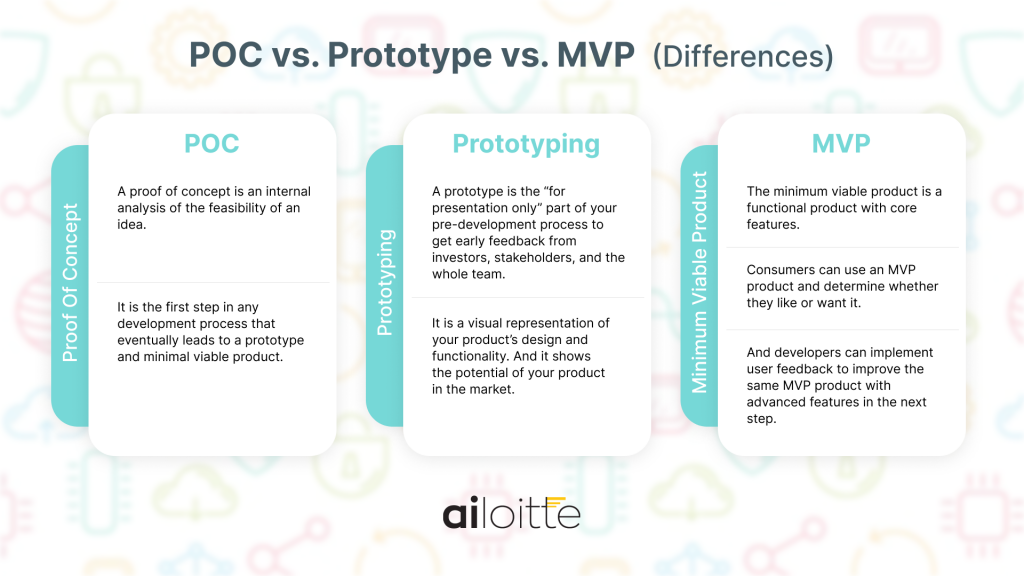
POC vs. Prototype vs. MVP: Differences
| Proof Of Concept (POC) | Prototyping | Minimum Viable Product (MVP) |
| A proof of concept is an internal analysis of the feasibility of an idea. It is the first step in any development process that eventually leads to a prototype and minimal viable product. | A prototype is the “for presentation only” part of your product to get early feedback for investors, stakeholders, and the whole team. It is a visual representation of your product’s design and functionality. It shows the potential of your product in the market. | The minimum viable product is a functional product with core features. Users can actually experience such a product and determine whether they like or want it. And developers can implement user feedback to create a more sophisticated product in the next step. |
Choose a Proof of Concept (PoC) If:
- You have to verify the feasibility of your idea before spending time, money, and effort on the development.
- You aim to create a new product with a unique strategy that no one has used or tested before.
- You hope to secure more investment by providing your product’s feasibility.
- You want to stand out from the competitors and offer something unique to users.
- You want every team member, investor, and stakeholder to add something to the final version of the product.
- When you have to check if the same idea has reached success in the past or not.
Choose a Prototype If:
- You want to show how your final product will look and perform.
- You have to get more investors interested in the potential of your product. You can do this by showing your product’s design and UX flow.
- You have less time to present the potential of your product to the whole team and stakeholders/investors.
- You want to get immediate feedback for effective improvement and development of your product.
Choose a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) If:
- You want to launch your product soon with core features that can meet user needs.
- You want comprehensive feedback that can provide better directions for further development.
- You want to begin generating revenue as you work on improvements.
- You want to identify the features that work for the user, those that do not, and features that can make the whole user experience even better.
MVP vs. Prototype vs. POC: Comparison
You can use MVP, Prototype, and POC in various stages of app/ software development process. But you have to know the exact point where you should use it to reap the benefits. Here are some tips to make things easy for you.
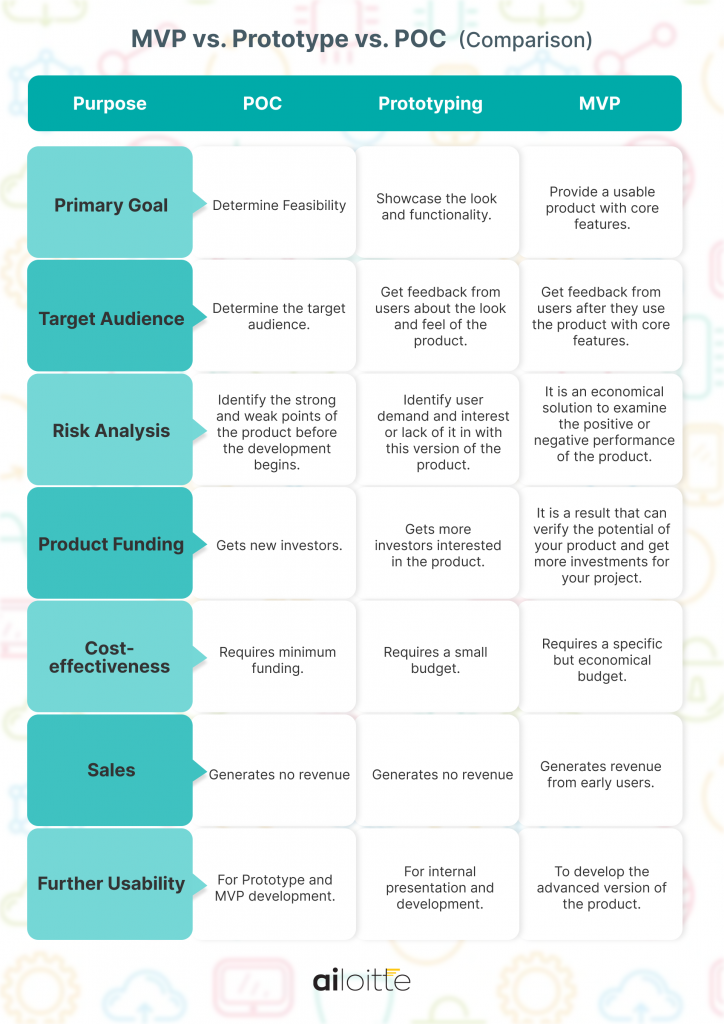
| Purpose | POC | Prototyping | MVP |
| Primary Goal | Determine Feasibility | Showcase the look and functionality | Provide a usable product with core features |
| Target Audience | Determine the target audience. | Get feedback from users about the look and feel of the product | Get feedback from users after they use the product with core features |
| Risk Analysis | Identify the strong and weak points of the product before the development begins. | Identify user demand and interest or lack of it in the version of the final product. | It is an economical solution to examine the positive or negative performance of the product |
| Product Funding | Gets new investors | Gets more investors interested in the product | It is a result that can verify the potential of your product and get more investments for your project |
| Cost-effectiveness | Requires minimum funding | Requires a small budget | Requires a specific but economical budget |
| Sales | No revenue | No Revenue | Generates revenue from early users |
| Further Usability | For Prototype and MVP development | For internal presentation and development | To develop the advanced version of the product |
Final Note
Proof of Concept (POC) vs Prototype vs MVP is a comparison that contributes to various stages of product/ app/ software development. In software development, they can direct the whole process of pre-development and development to ensure success for the final product.
You must consult a software and mobile app development company before executing any of the three strategies in your development project.
Such a company understands the practical working concepts of POC, Prototyping, and MV. And will help you execute them with professional finesse.
Get in touch with our experts to get exclusive assistance with all three strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
A prototype is a visual presentation of a product idea to show its potential to the internal team, investors, stakeholders, and target audience. It also provides early product feedback from the same groups.
The minimum viable product is a functional product with core features that users can experience. Unlike a prototype, it’s a basic version of a usable product that generates money.
Proof of Concept comes before the prototype. POC is a process that determines the feasibility of an idea. And prototyping is a visual representation of that analysis to showcase the product design and functionality.
Proof of Concept (POC) evaluates the feasibility of a product idea in practical applications, its potential, and the risks associated with the development process. It helps you understand whether you have more to gain or lose by moving forward with the development process.
A good POC analysis of your idea also helps you get investors to support the funding of your project.
No, they are not. POC is a process that determines the practicality of your idea in real-world applications. It is an internal process and does not involve any actual development.
MVP is the first and basic iteration of the product with core features. It verifies the POC analysis by getting the predicted results. Unlike POC, MVP involves actual development and product launch. It also generates money and paves the way for the advanced version of the product.


















.png)
.png)
.png)



Leave a Comment